With osteochondrosis, the spinal structure undergoes degenerative-dystrophic changes, which are accompanied by violations of the anatomical structure of the intervertebral disc, as well as its functionality. One of the common forms of the disease is cervical spinal osteochondrosis.
If you believe in statistical data, then more than half the world's population has one degree or another severe pathological manifestation. As a rule, the average age of the main manifestation of the disease occurs for 30-40 years.
In cases where poor living conditions, genetic predisposition and provocative factors are combined, the development of osteochondrosis can reach the age of 20-30 years. Especially if this is facilitated by prolonged static loads in the spinal ridge or different back injuries.
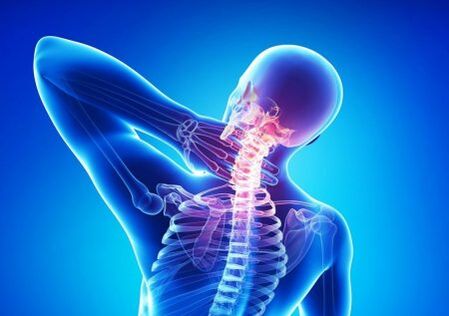
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous? Complications and consequences, can a person die from illness?
A general clinical picture
IMPORTANT! The main provocator of pathological formation is an uneven burden on the spinal column. This can happen because wearing heavy bags on just one shoulder or just in one hand, sitting inside, from the spine, pose, very soft mattress use, large feathers for sleep, wearing high heels and very high. All of this leads to the wrong distribution of loads on the spine.
In addition, the negative effects are on:
- hypodynamia;
- SEDENTARI LIFE;
- obesity;
- spinal injury, pelvic bone or limbs;
- Pathological changes in foot sets;
- Age aspect.
Other causes affecting the development of the disease include:
- excessive physical activity;
- chronic psycho stress;
- disorders of metabolic processes;
- any kind of poisoning;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- Professional damage (for example, these include labor on the vibration platform);
- genetic factors;
- Formation of posture violations, scoliosis during the period when the frame is in an active phase of growth;
- Improper shoes (very narrow, high heels);
- insufficient use of fluid;
- Improper and low nutrition, lack of adequate entry to the body of all the vitamins and trace elements needed for it;
- chronic nicotine intoxication;
- The duration of pregnancy, as this condition is characterized by the center of gravity.
What threatens cervical spinal osteochondrosis in women?
The main clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis:
- pain in the neck, shoulder, ribs;
- feelings of discomfort, stiffness in the movement of the body (changes in its position, tendency, head change);
- Hypertonicity of the muscle or, on the other hand, hypotonus;
- numbness in the area of the hands, hands and fingers;
- headache, dizziness;
- symptoms of asthenia;
- Strong pain;
- paresthesia in the upper foot zone;
- appearance of spots -the spots in front of the eyes;
- The sound of sound in the ear.
Doctor's opinion:
Cervical osteochondrosis is a serious disease that can cause a variety of complications if you do not pay attention to it. The doctor notes that the main causes of the development of this condition are associated with improper posture, sitting lifestyle, excessive pressure in the cervical spine. Symptoms of osteochondrosis can include pain in the neck, headache, dizziness, numbness in the hands. Often, the patient complains of stiffness in the neck and shoulders. Doctors warn that ignoring these symptoms can cause nerve compression, blood circulation disorders, and also to the development of intervertebral disc hernia. Therefore, it is important to contact the specialist on time for diagnosis and prescribe complex treatments, including medication, physiotherapy and special training.
Spinal lesions
The pathological process course can be divided into four stages:
- During this time, the major changes in the nucleus pulpoose of the intervertebral disc begins. Large loads lead to nucleus dehydration, where the amount of intervertebral disc decreases and cracks in fibrous rings occur. This level usually has no clinical manifestations. One of the most alarming symptoms may be a sense of discomfort during active movement performance or staying in an uncomfortable position.
- The continuous reduction in discs will contribute to the reduction of intervals between the neighboring vertebrae, as well as to continue the muscle and spinal ligaments. These changes will lead to the fact that the affected vertebrae and disc becomes more mobile, which is full of displacement or slipping. Here, the patient has complained about the incidence of pain, which is provoked by changes in the body's position, by searching in several pose, and the influence of the load.
- At this stage, the affected disk prolapse or prominence will occur. Which is often accompanied by the formation of joint subluxation or spinal joint arthrosis. Patients begin to complain about the occurrence of restrictions in the performance of various movements, stiffness, paresthesia or numbness at the top. The pain syndrome, a localized localization, becomes more intense and requires taking medication to relieve it.
- The body does everything possible to overcome the results of an increased individual vertebra movement, adapting to the new condition of existence associated with the violation of the normal functioning of the spinal structure. In areas where the vertebrae comes in contact with each other, the growth of bone tissue (osteophytes formed) for more reliable fixation occurs. But there are frequent cases when bone growth triggers vertebral injuries, vascular-Naval beam compression. The formation of fibrous ankylosis of the intervertebral joint occurs. If there is no injury or compression of the nerve endings, the severity of the clinical manifestation can be slightly faded.
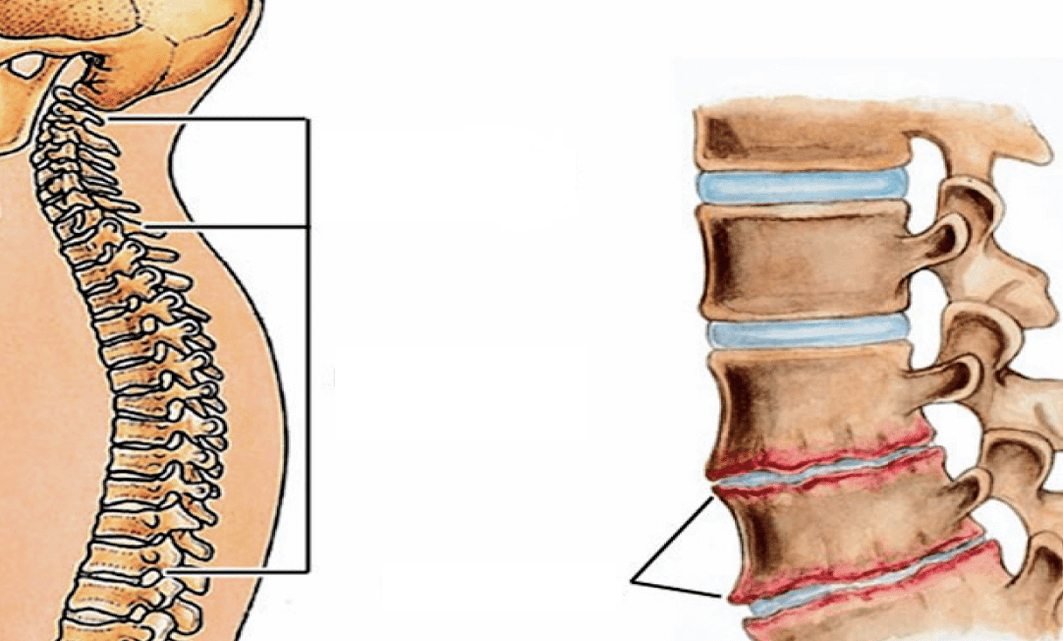
Neurological symptoms: headache, neck and back pain, effects on the brain
A violation of the vegetable system
Degenerative changes in vertebrae lead to violations of their structure. With the development of the disease, changes begin to affect the vascular and nervous structure of the spine.
Attention! Nerve root irritation causes vascular cramps (vasoconstrictor affects the artery), resulting in the transportation of oxygen and nutrients to the brain. Neuron ischemia leads to a violation of certain hormone production, a task that includes ensuring the normal functioning of the vegetative system.
The result will be the development of the symptoms of vegetable dystonia:
- fluctuations in blood pressure;
- pain in the temple;
- difficulty or inability to take a long breath;
- dizziness, syncopal state;
- Tachycardia;
- pain behind the sternum;
- pain in epigastria;
- Hyperhidrosis;
- The appearance of the shaking hands.
The experience of others
Cervical osteochondrosis is a serious disease that is widely discussed. It is dangerous as it can lead to a variety of complications, including disorders of blood circulation in the brain and spine. At the same time, the consequences can be very serious, to the paralysis of the limbs. The cause of the development of the disease can be an improper posture, an inactive lifestyle, neck injury, infection. Symptoms include headaches, dizziness, ear noises, tingling sensations in the hands. Therefore, it is important to contact a specialist at the first signs to avoid possible complications.
Hypertension and hypotension
Compression of the radical nerve structure in the cervical region causes a violation of vascular conservation. Continued compression of the nerve tissue leads to the fact that fiber loses the ability to perform impulses from the cerebral structure of the brain pyramid.
Attention! In advanced cases, vertebral artery syndrome can be formed. In this case, both hypotonic and hypertension conditions may occur.
With a combination of osteochondrosis with high levels of vertebral damage and blood pressure fluctuations, the approach to therapy for conditions should be complex. If only a cardiologist treats the patient, then he will not achieve stress normalization. This may be subject to the effects of the pathological change in the spine. In the absence of an integrated approach, sharp compensation jumps in pressure may occur, which causes the development of spinal ischemia or hemorrhagic stroke.
Dangers of damaging effects on the spine
Headache and nervous system affected
Pain in the head area is one of the common symptoms of this pathology. The use of painkillers has a positive effect only for a short period of time, but there is no elimination of the main cause of the disease.
The main factor leading to the occurrence of pain is the subluxation formed from the neck vertebra. In this case, there are compression of the vertebral artery and nearby nerve fibers.
Headaches are common. The following symptoms may accompany him:
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- Tinnitus;
- dark in front of the eyes;
- short loss of consciousness;
- irritation;
- insomnia;
- Reduce performance.
Syndrome
In the osteochondrosis clinic, the following syndrome complex is distinguished:
- cervical vertebrogenic syndrome compression-brown;
- Irritating pain syndrome; muscles;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- Myelopathy cervical compression.

The effects of therapeutic therapeutic and the use of therapeutic drugs, their harmful effects on the joints
How to prevent pathology
To prevent the disease from developing, it is enough to regularly do a set of exercises. Estimated options for morning or evening gymnastics:
- Press your forehead in the palm of your hand and tighten your neck muscles. It is required to take three approaches for seven seconds. Then change the direction and press the back of the head in the palm of your hand. The number of approaches is the same.
- Press the left temporal area in the left palm, and then repeat the exercise for the right side. In this case, you do not need to forget to repel the cervical muscles.
- The head throws a little back. Next, you need to press the chin to the jugular fossa, overcoming the resistance of tense muscle fibers. The number of approaches is five.
- Head and shoulder belts are straightened. It is required to make a head turn to the maximum amplitude that may first to the right, and then to the left.
- The chin sinks into the neck. And the head is also made first in one direction, and then in the other.
- The head threw back. It is required to make contact with the right ear of the right shoulder, and then vice versa.
All exercises are done five times on each side. They can be done at home and at work. Especially if work is associated with a large load on the neck. The starting position can also be selected: stand or sit on the chair. What you can't do is do the head circular movement, as you can trigger the vertebra.
Treatment Outcomes: To what extent you can get rid of the disease, the possibility of complications of the disease and the consequences are dangerous to live
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease that will not occur over time. Modern medicine cannot cure degenerative vertebral changes. Therefore, the job of the patient and the doctor is to prevent the development of pathology and complications.
Frequent questions
What can be the result of cervical osteochondrosis?
What is a dangerous cervical osteochondrosis if you do not take timely treatment, as a result of the disease can violate cerebral circulation, weakness and muscle atrophy, function of organ disorders and internal systems. The disease also leads to limiting spinal mobility and loss of hand sensitivity.
What helps with cervical osteochondrosis well?
Painkillers are effective in the form of gels, ointments, tablets, injections that are contraindicated to children, as well as women during pregnancy and lactation.
What does someone feel with cervical osteochondrosis?
With "cervical osteochondrosis" in the neck, visible muscle atrophy (muscle weight loss), decrease or increased muscle tone -long -term muscle tone, and static violations in the cervical region can be observed.
Why is cervical osteochondrosis dangerous?
The dangers of cervical osteochondrosis in advanced osteochondrosis levels can develop ischemia, stroke and many other harmful diseases to human life. Therefore, when any symptoms associated with the disease arise, it is recommended to seek medical help.
Tips are useful
Council No. 1
Maintain proper posture and avoid staying in the wrong position to reduce the load on the cervical spine.
Council No. 2
Regular exercise for the neck and returns to strengthen the muscles and increase the flexibility of the joints.
Council No. 3
Avoid lifting weights without proper technique so as not to load the cervical spine and does not worsen osteochondrosis.